Unlike other long-term assets such as machinery, buildings, and equipment, land is not depreciated. The process to calculate the loss on land value could be very cumbersome, speculative, and unreliable; therefore, the treatment in accounting is for land to not be depreciated over time. Notes receivable is similar to accounts receivable in that it is money owed to the company by a customer or other entity. The difference here is that a note typically includes interest and specific contract terms, and the amount may be due in more than one accounting period. Insurance, for example, is usually purchased for more than one month at a time (six months typically).
Therefore, the company must record the usage of electricity, as well as the liability to pay the utility bill, in May. Before we explore how to analyze transactions, we first need to understand what governs the way transactions are recorded. Shaun Conrad is a Certified Public Accountant and CPA exam expert with a passion for teaching. After almost a decade of experience in public accounting, he created MyAccountingCourse.com to help people learn accounting & finance, pass the CPA exam, and start their career.
Remember that the accounting equation must remain balanced, and assets need to equal liabilities plus equity. On the asset side of the equation, we show an increase of $20,000. On the liabilities and equity side of the equation, there is also an increase of $20,000, keeping the equation balanced. Changes to assets, specifically cash, will increase assets on the balance sheet and increase cash on the statement of cash flows.
For instance, corporations have stockholders and paid-in capital accounts; where as, partnerships have owner’s contribution and distribution accounts. Thus, all of these entities have a slightly different expanded equation. The fundamental accounting equation is debatably the foundation of all accounting, specifically the double-entry accounting system and the balance sheet. Double-entry accounting is the concept that every transaction will affect both sides of the accounting equation equally, and the equation will stay balanced at all times. The accounting equation, whether in its basic form or its expanded version, shows xero integration with quote roller the relationship between the left side (assets) and the right side (liabilities plus capital). It also shows that resources held by the company are coupled with claims against them.
When Should I Use the Basic Accounting Equation?
When dividends are issued, cash is disbursed to shareholders reducing assets while the dividends reduce equity. Short and long-term debts, which fall under liabilities, will always be paid first. The remainder of the liquidated assets will be used to pay off parts of shareholder’s equity until no funds are remaining.
A notes payable is similar to accounts payable in that the company owes money and has not yet paid. The accounting equation emphasizes a basic idea in business; that is, businesses need assets in order to operate. There are two ways a business can finance the purchase of assets. First, it can sell shares of its stock to the public to raise money to purchase the assets, or it can use profits earned by the business to finance its activities. Second, it can borrow the money from a lender such as a financial institution.
The equation layout can help shareholders to see more easily how they will be compensated. For another example, consider the balance sheet for Apple, Inc., as published in the company’s quarterly report on July 28, 2021. Adam Hayes, Ph.D., CFA, is a financial writer with 15+ years Wall Street experience as a derivatives trader. Besides his extensive derivative trading expertise, Adam is an expert in economics and behavioral finance.
Accounts shows all the changes made to assets, liabilities, and equity—the three main categories in the accounting equation. Each of these categories, in turn, includes many individual accounts, all of which a company maintains in its general ledger. The company has yet to provide the service, so it has not fulfilled the obligation yet. According to the revenue recognition principle, the company cannot recognize that revenue until it meets this performance obligation or in other words provides the service.
Introduction to the Accounting Equation
Cash includes paper currency as well as coins, checks, bank accounts, and money orders. Anything that can be quickly liquidated into cash is considered cash. Cash activities are a large part of any business, and the flow of cash in and out of the company is reported on the statement of cash flows. Here is the expanded accounting equation for a sole proprietorship. As was previously stated, double-entry accounting supports the expanded accounting equation.
- Even though the company does not have to pay the bill until June, the company owed money for the usage that occurred in May.
- Essentially, anything a company owes and has yet to pay within a period is considered a liability, such as salaries, utilities, and taxes.
- The expanded equation is used to compare a company’s assets with greater granularity than provided by the basic equation.
- For the past 52 years, Harold Averkamp (CPA, MBA) has worked as an accounting supervisor, manager, consultant, university instructor, and innovator in teaching accounting online.
Expanded Accounting Equation
Textbook content produced by OpenStax is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike License . Take your learning and productivity to the next level with our Premium Templates. Access and download collection of free Templates to help full bookkeeping denver power your productivity and performance. Rearrangement in such a way can be useful when looking at bankruptcy.
Accounting Equation Outline
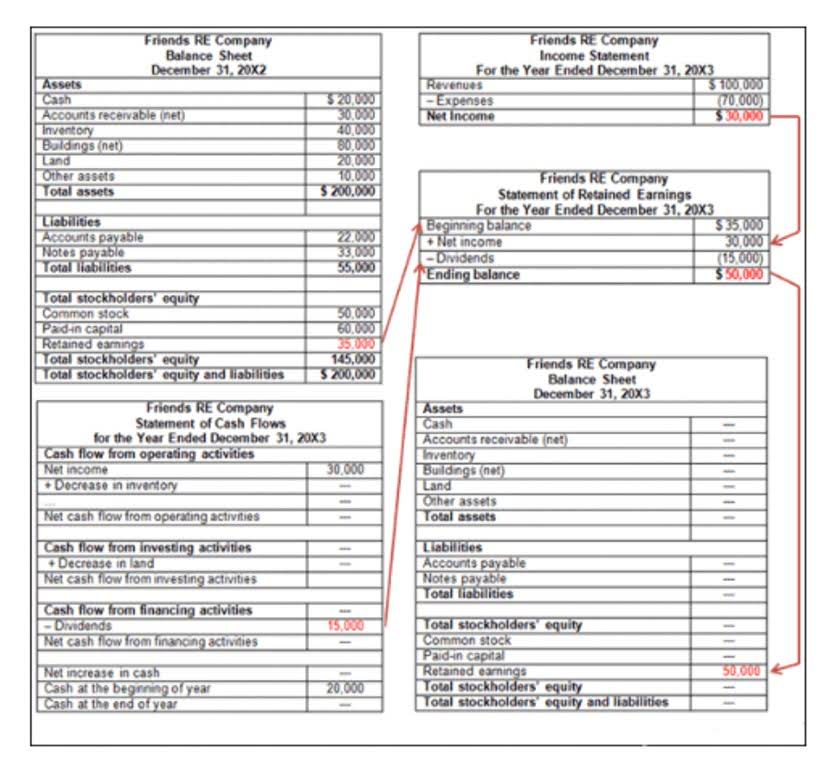
Net income (loss) is computed into retained earnings on the statement of retained earnings. This change to retained earnings is shown on the balance sheet under stockholder’s equity. You will notice that stockholder’s equity increases with common stock issuance and revenues, and decreases from dividend payouts and expenses. Stockholder’s equity is reported on the balance sheet in the form of contributed capital (common stock) and retained earnings. Now, we can consider some of the transactions a business may encounter. We can review how each transaction would affect the basic accounting equation and the corresponding financial statements.
This expanded equation takes into consideration the components of Equity. Equity increases from revenues and owner investments (stock issuances) and decreases from expenses and dividends. These equity relationships are conveyed by expanding the accounting equation to include debits and credits in double-entry form. The balance sheet is also known as the statement of financial position and it reflects the accounting equation. The balance sheet reports a company’s assets, liabilities, and owner’s (or stockholders’) equity at a specific point in time.
2 Define and Describe the Expanded Accounting Equation and Its Relationship to Analyzing Transactions
The company does not use all six months of the insurance at once, it uses it one month at a time. As each month passes, the company will adjust its records to reflect the cost of one month of insurance usage. The expanded accounting equation can be rearranged in many ways to suit its use better. With that being said, no matter how the formula is laid out, it must always be balanced. This results in the movement of at least two accounts in the accounting equation.
Because there are two or more accounts affected by every transaction, the accounting system is referred to as the double-entry accounting or bookkeeping system. Examples of assets include cash, accounts receivable, inventory, prepaid insurance, investments, land, buildings, equipment, and goodwill. From the accounting equation, we see that the amount of assets must equal the combined amount of liabilities plus owner’s (or stockholders’) equity.










Recent Comments